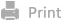Intelligent micelles for on-demand drug delivery targeting extracellular matrix of pancreatic cancer
Time:2024/10/20 15:29:20 Views:215
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most deadly tumors, in which the key pathological features of dense extracellular matrix (ECM) limit the penetration of chemotherapy drugs and participate in the formation of tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment. At the same time, clinical practice has suggested that treatment strategies targeting ECM should consider its limitations on tumor cell metastasis, and the need for deep chemotherapy without destroying ECM has been proposed.
Signal transduction factor and transcriptional activator 3 (STAT3) molecule plays a key role in the progression of PDAC. STAT3 performs complex functions in the tumor microenvironment of PDAC through phosphorylation and nuclear translocation in various cells. STAT3 can promote the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells, enhance their anti-apoptotic ability, and mediate the formation of ECM in pancreatic stromal cells. In addition, recent studies have shown that STAT3 is involved in the construction of immunosuppressive microenvironment by promoting the release of various cytokines to recruit immunosuppressive cells. Extensive inhibition of STAT3 molecules in the tumor microenvironment, thereby enhancing the ability of chemotherapy drugs to induce apoptosis, and remodeling ECM and immune microenvironment may be a promising treatment for PDAC.

Scheme 1. Schematic illustration of the construction of micelle MP@HA
Based on the above characteristics, our research group designed an intelligent micelle MP@HA that can co-deliver chemotherapy drugs and STAT3 inhibitors on demand to the extracellular matrix of pancreatic cancer, and has the function of in vivo targeting and responsive drug release. The micellar system co-carries gemcitabine monophosphates and silybin, a STAT3 inhibitor. Hyaluronic acid on the surface of micelles can bind specifically to CD44 molecules on the surface of tumor cells, helping micelles to accumulate at the tumor site. By modifying the polymer skeleton with nitroimidazole, the micellar structure of the polymer was collapsed under hypoxic reduction conditions in the tumor environment, and silybin was released, which extensively regulated STAT3 molecules in the PDAC microenvironment. Gemcitabine monophosphate attached by polymer fragments due to small size and surface positive charge, can penetrate into PDAC tumor tissue and realize deep chemotherapy. Through in vivo and in vitro experiments, the micelle can achieve chemotherapy sensitization, reshape ECM, and improve the immunosuppressive microenvironment. This study provides a promising drug delivery system for antitumor therapy of PDAC.

Scheme 2. Schematic illustration of MP@HA for PDAC treatment.
The article entitled“ Intelligent micelles for on-demand drug delivery targeting extracellular matrix of pancreatic cancer.” has been published on “Journal of Controlled Release”.
Chufeng Li, the 2021 graduate student in our research group, is the first author of the paper, and Professor Chen Jiang is the corresponding author of the paper. The research was supported by Zhang Jiang's lab.
Full-article link:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365924005169?via%3Dihub